Encoding and decoding are key principles in digital media comprehension and interaction. While These processes are generally overlooked by the typical user, instead they are fundamental in how we consume, interact with, and comprehend digital material.
The Essential of Encoding and Decoding
Encoding in digital media refers to the conversion of content – whether text, sound, or image – into a digital format. The process is needed for effective storage, transmission, and interaction across systems or devices. Decoding is the process of transforming encoded data back into a format that we, the end users, can understand and access.
Theoretical Underpinnings
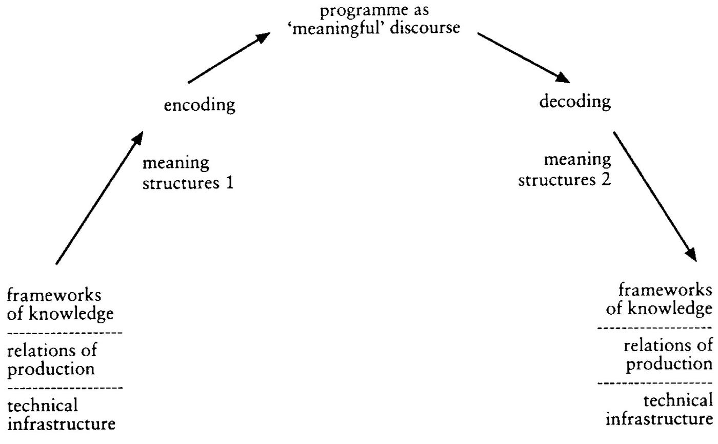
When it comes to theory, the encoding/decoding model is developed by cultural theorist Stuart Hall, provides important insights. According to Hall’s concept, communication involves not only transmission but also interpretation. In that regard, encoding includes not only the mechanical translation of data but also the sender’s symbolic encoding of meaning. Decoding is how the audience analyses the message, impacted by their own cultural settings and experiences. This model highlights that meaning in communication is not fixed but can be interpreted differently as it passes from sender to recipient.
Real-World Applications
Every photo, video, or text we publish to social media sites is encoded for internet transmission and is then decoded by the devices of other users. For instance in streaming services like netflix or youtube.
Encoding and decoding impact the public’s understanding and engagement in digital media. The way news is delivered and perceived on digital platforms has the potential to change public perception. In interactive media, such as online gaming, the encoding of game data and its decoding for real-time play exemplify the dynamic nature of these processes.

Technological Innovations and Challenges
Technological advancements in encoding and decoding, like multiple watermarking in digital images, enhance security and tracking in multimedia. However, these advancements also bring challenges in maintaining the integrity and intended meaning of the encoded content.

Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of encoding and decoding in digital media is critical for holding the complexity of our linked digital world. These are not only technological processes; they are linked to how humans communicate and receive information. As digital media evolves, so will these underlying processes, influencing the future of digital communication and interaction.
Reference
Murdock, G. (2017). Encoding and decoding. The International Encyclopedia of Media Effects, 1-11.
B├Ėdker, H. (2018). Stuart HallŌĆÖs encoding/decoding model and the circulation of journalism in the digital landscape. In Stuart Hall Lives: Cultural Studies in an Age of Digital Media (pp. 57-71). Routledge.
Shaw, A. (2017). Encoding and decoding affordances: Stuart Hall and interactive media technologies. media, culture & society, 39(4), 592-602.
Palmer, M. (2020). Facebook as a meta-ideological apparatus: reassessing the encoding/decoding model in the context of social media (Doctoral dissertation).
